4WD
Contents
hide
Overview
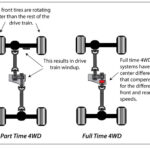
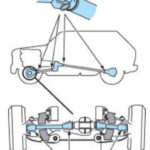
Part Time 4WD
Driver Input
- Requires driver input to activate
Modes
2WD mode
- Main mode, for everyday pavement use.
- Usually only rear wheels are powered.
- In some cases front wheels are powered instead
4WD mode
- 4WD “high”
- 4WD “low”
- Does not provide more traction.
- Provides 2-3 times more torque at about 1/2-1/3 of the speeds in high range.
- If the vehicle has manual locking hubs on the front wheels, they need to be locked first.
- Used part of the time.
- Very good on tough terrain or off-roading.
- Torque is divided between front and rear drive-shafts (50/50 fixed)
- ⚠️ Important. Not meant to be driven in 4WD (4WD-Hi or 4WD-low) on high-traction surfaces (dry pavement) or severe damage will occur (because vehicle does not have a center differential to allow different speeds between front and rear axles)
- ⚠️ Important. Tires must be of the same size and have the same tread wear.
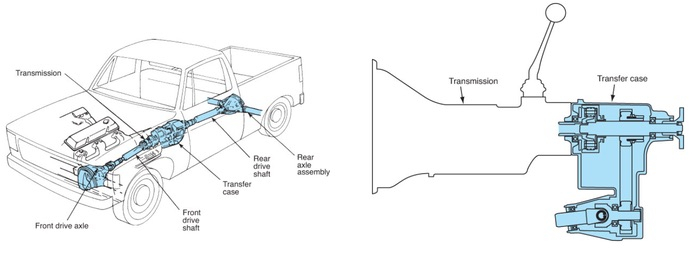
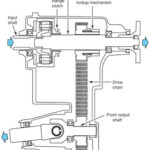
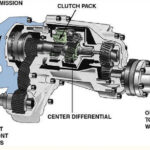
Components
- transfer case with 2-speed capability
- two drive shafts
- two axle differentials
- No center differential!
- Shifting back to 2WD will become impossible (gears and levers are extremely forced together).
Full-Time 4WD, AWD
Driver Input
- No input from the driver needed.
Modes
4WD “low”
- Full time 4WD: Might have 4WD LOW when needed for towing, and some off-road crossing.
- AWD: Doesn’t have 4WD LOW
4WD “high”
- 4WD system that can be used on all surfaces (addition of a differential in the transfer case allows for the Full-Time 4WD)
⚠️ Important. Tires must be of the same size and have the same tread wear.
Components
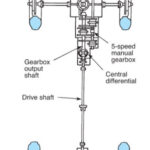
- Usually center differential (usually viscous coupling) instead of a transfer case
- Open or limited-slip center differential
- Limited-slip differential at the rear.
- Might have , limited-slip differential at the front.
- Traction problems
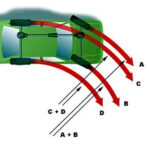
- Nature of a differential is to direct all an engine’s torque down the path of least resistance—the tire with the least grip.
- On a turn, left and right wheel spins differently.
- Front wheels travel further than rear wheels.
- Nature of a differential is to direct all an engine’s torque down the path of least resistance—the tire with the least grip.

- 4WD Auto
- Full power to the rear wheels. Front wheels receive power as required.
- 4WD HI
- Full power to all wheels. No center gear reduction.
- 4WD LO
- Low gear ratio in the center differential (2:1) for slow, high torque driving.
On demand 4WD, Automatic AWD
- combination of AWD and Part Time 4WD
Driver Input
- Drive should be able to choose an “AWD” mode
- Generally will allow driver to choose several different 4WD modes, including 2WD.
Modes
2WD mode
- Under normal conditions one axle gets 100% of the torque.
4WD mode
- Limited 4WD off-road.
- Engages only after slip is detected
- During traction loss at the driven axle (could be front or rear) a fully automatic system (hydraulic, mechanical or electronic) makes some of the torque to the axle with traction available.
- This means you have to lose traction in 2WD on your driven axle first and then the other axle will be added and try to keep the car moving and stable.
- Once the primary driven axle regains traction and both axles rotate at the same speed again, the system reverts back to 2WD.
- Important. Tires must be of the same size and have the same tread wear.
Components
- Center Differential: Manual or Viscous Coupling
Transfer Case
- Auxiliary transmission mounted to the side or rear of the main transmission
- No differential action is provided
Types
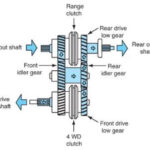
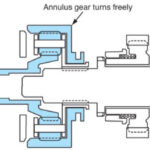
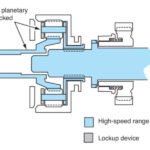
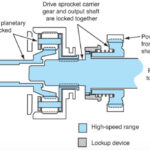
Ranges of Operation (part time transfer case)
Differential
Overview
Center Differential for AWD and 4WD
Types
Open Type
- If wheels on either final differential loose traction, maximum torque is delivered to the axle with a LEAST traction.

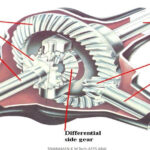
Limited Slip Type
- Traction
- The standard differential delivers maximum torque to the wheel with minimum traction.
- The limited slip differential delivers maximum torque to the wheel with maximum traction.
- Types
- Clutch Pack
- Cone Clutch
- Torsen
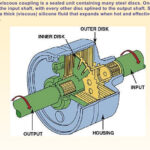
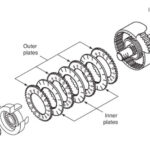
- Viscous Coupling
- When the two sets of plates are rotating in unison, the fluid stays cool and remains liquid.
- When the plates start rotating at different speeds, the shear effect of the tabs or perforations on the fluid will cause it to heat and become nearly solid because the viscosity of dilatant fluids rapidly increases with shear. The fluid in this state will effectively glue the plates together and transmit power from one set of plates to the other. The size of the tabs or perforations, the number of plates, and the fluid used will determine the strength and onset of this mechanical transfer.

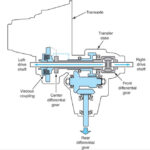
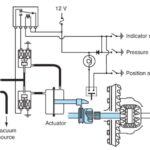
Active/ Electronic Type (both open and locked)
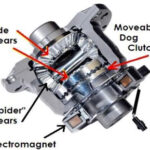
- Dynamically locks differential using electro-magnetic clutch.
- Signals used:
- Steering wheel angle sensor
- ABS sensors
- Engine rpm
- 4. Locking
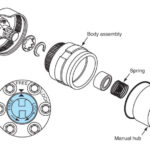
Locking Hubs
- Used on older vehicles.
- Unlocking hubs when not need is advocated based on debatable benefits: better fuel efficiency, quieter operation, less vibration, and lower wear.
Manual
Automatic
- Vacuum or electro-magnetically operated.
-
- Automatically locks when the speed difference between the wheels and the front axle is great.
- Unlocked by disengaging four-wheel drive and driving in reverse for several feet.
- Disadvantage. They don’t transfer torque to the front wheels in reverse.
Universal Joints or CV Joints
Manufacturer-Specific Notes
BMW
📎 5463 VTG Mechanism | Bad VTG Motor | E53 | 2006’ X5
- VTG: 5463 VTG mechanism faulty


- New part (link)
📎 VTG Codes | 2015 BMW 320xi (F30)
- Had abs, traction, and brake lights on
- VTG codes
- 440115 Transfer Box (VTG): calibration angle deviation outside tolerance
- 44011B Transfer Box (VTG): Torque delivered outside torque characteristic
- ABS codes
- 480682 Transfer Box: Fault, clutch position unknown
- 48097D Transfer Box: Fault, clutch position known, no four wheel drive
- D36D44 Transfer Box: Signal (longitudinal torque distribution, front axle/rear axle, 19.3.4) invalid, transmitter VTG
- VTG codes
- Replaced transfer case. Only traction light remained. No VTG codes. ABS code was same/similar to
- 48097D Transfer Box: Fault, clutch position known, no four wheel drive
- Reprogrammed/Coded VTG. Codes and light went away.
GM
Rear Differential Module
- Replacing Rear Differential Module requires an SPS Programming and performing a Setup function.
- Setup function will ask for “Rank ID”, two digits, its stamped on the plastic case of one of the two connectors (smaller one) that plugs into rear differential module (aka 87).